

Lab-grown diamonds are authentic diamonds, created by replicating the natural force of the Earth within a controlled laboratory environment. Starting from a single diamond 'seed,' advanced technology—such as Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)—simulates high heat and pressure to crystallize carbon into a gemstone that is physically, chemically, and optically identical to an earth-mined diamond.
This modern approach to luxury offers a transparent, conflict-free supply chain, ensuring that every stone is as ethical as it is beautiful. Because they are grown under optimized conditions, these diamonds often exhibit superior purity and consistency, providing a high-performance and cost-effective alternative for the global jewelry market. At DSons Impex, we recommend all significant stones be accompanied by an independent grading report, such as from the GIA or IGI, to certify their exceptional quality and authenticity.
Lab-grown diamonds are rapidly becoming the preferred choice for the modern luxury market. By combining advanced science with ethical craftsmanship, they offer a superior alternative to earth-mined stones without compromising on brilliance or integrity. The key advantages include: Superior Purity & Optical Performance Our controlled CVD growth process results in Type IIa diamonds—the purest form available—exhibiting exceptional light performance and clarity. Guaranteed Ethical Provenance With a fully transparent supply chain, our diamonds are 100% conflict-free, offering peace of mind through responsible and modern manufacturing. Exceptional Value & Creative Scale The cost-efficiency of lab-grown stones allows partners to offer larger carats and higher quality grades while maintaining competitive market pricing. Sustainable & Environmentally Conscious By eliminating the need for traditional mining, we significantly reduce the environmental footprint, preserving the planet for future generations.


.webp)
At world-class gemological laboratories, independent experts rigorously evaluate every diamond using the universal 4Cs: Cut, Clarity, Color, and Carat. For lab-grown diamonds, obtaining a third-party certificate is essential to guarantee both authenticity and market value. DSons Impex works with the industry's most prestigious grading authorities, with a primary focus on IGI and GIA standards.
Leading Certification Authorities:
International Gemological Institute (IGI)
As the global leader in lab-grown diamond certification, IGI provides the most detailed and widely accepted reports for the CVD and HPHT market.
Gemological Institute of America (GIA)
Known as the world’s foremost authority on gemology, GIA offers specialized reports that certify a lab-grown diamond’s technical specifications.
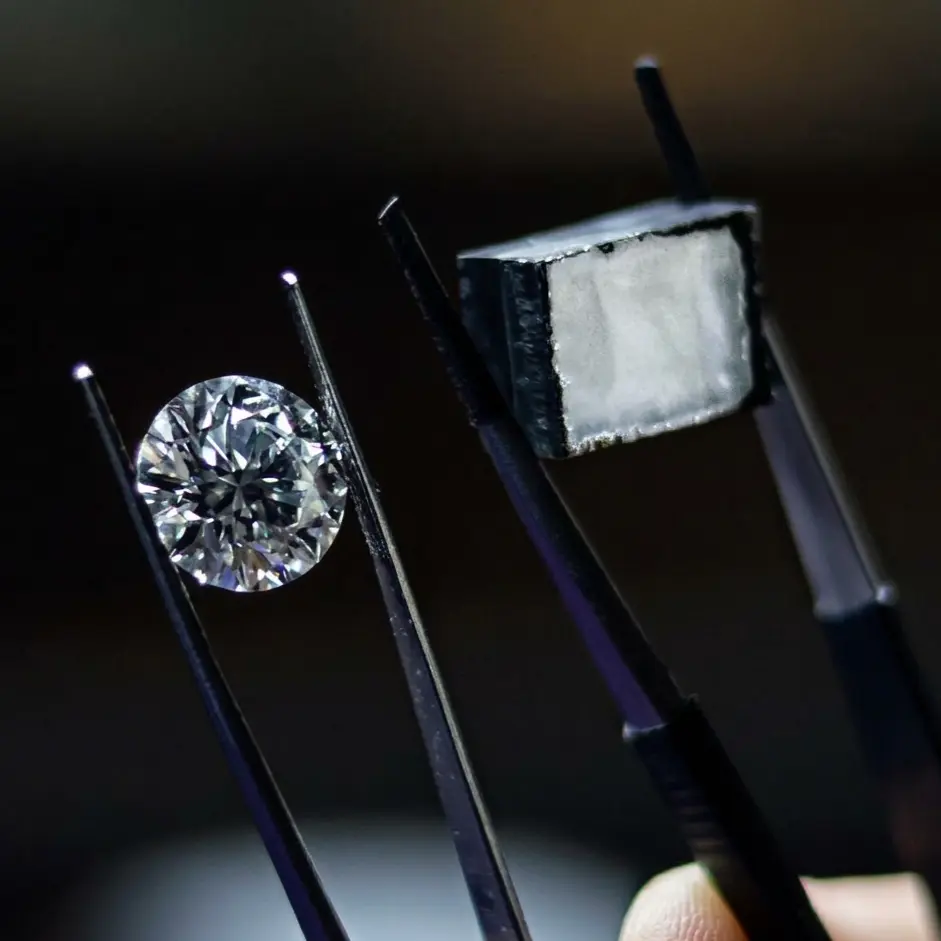
The only difference between a lab-grown diamond and an earth-mined diamond is its point of origin. Earth-mined diamonds formed billions of years ago under geological pressure, while lab-grown diamonds are cultivated using the same carbon-crystallization process in a controlled environment.
From a physical, chemical, and optical standpoint, lab-grown diamonds are identical to their naturally occurring counterparts. They exhibit the same hardness, brilliance, and fire, making them indistinguishable even to most experts without specialized laboratory equipment. At Dsons Impex, we specialize in high-purity stones that offer the same lasting beauty and durability as mined diamonds at a more accessible value, allowing for greater design possibilities in high-end jewelry.



At Dsons Impex, we utilize the two most advanced scientific methods to cultivate diamonds that are chemically and physically identical to those found in nature. By precisely replicating the Earth's natural conditions, we grow high-purity diamonds with absolute consistency.
1. HPHT Method (High Pressure High Temperature)
Natural Replication: This method recreates the extreme environment found 100 miles below the Earth's surface, where temperatures exceed 1,500°C and pressures reach 1.5 million psi.
The Growth Process: Using advanced hydraulic presses—such as cubic or split-sphere technology—a diamond seed is placed in pure carbon and subjected to these intense forces until it crystallizes into a raw gemstone.
Primary Use: HPHT is exceptionally effective for growing large, high-quality diamonds and is also used to enhance the color of certain stones.
2. CVD Method (Chemical Vapor Deposition)
Modern Precision: CVD is a specialized technique that grows diamonds from a hydrocarbon gas mixture in a vacuum chamber.
Plasma Technology: A diamond seed is heated and exposed to carbon-rich gases, which are ionized into plasma. This causes pure carbon atoms to adhere to the seed.
Atom-by-Atom Growth: The diamond grows layer-by-layer, atom-by-atom. This controlled environment allows for the production of Type IIa diamonds, the rarest and most chemically pure category.
Key Improvements Made:
Vocabulary Shift: Replaced "Synthetic Replication" with "The Growth Process" or "Advanced Engineering." This avoids the "fake" connotation of the word synthetic.
Technical Details: Added specific metrics like "1,500°C" and "Type IIa" to showcase your technical expertise to professional buyers.
Correction: Fixed the spelling of "Culet" (written as "Cutlet" in your earlier draft) and "Girdle" (written as "Gridle") in the structural descriptions to ensure professional accuracy.